Project Migration
Migrating from a monolithic architecture to a microservices architecture involves careful planning, design, and execution. Here are the steps to guide you through the process:
Assessment and Planning:
- Understand the monolithic application’s architecture, components, dependencies, and pain points.
- Define the goals and reasons for migrating to microservices. Identify the expected benefits.
- Assess the feasibility of breaking down the monolith into microservices considering technical challenges and potential advantages.
Identify Microservices:
- Identify cohesive and well-defined components within the monolith that can be extracted into microservices.
- Focus on areas that experience high changes, scalability issues, or where independent deployment is crucial.
Define Service Boundaries:
- Determine clear boundaries for each microservice to avoid tight coupling and minimize dependencies.
- Define the API contracts/interfaces that microservices will expose to communicate with each other.
Design Microservices:
- Design each microservice as an independent unit with its own data store, logic, and responsibilities.
- Choose appropriate programming languages, frameworks, and technologies for each microservice.
- Ensure a consistent naming convention and versioning for APIs.
Data Management:
- Decide how data will be managed and shared among microservices. Consider using database per service or shared data stores if necessary.
- Plan data synchronization mechanisms, considering eventual consistency and data ownership.
Communication and Integration:
- Choose communication mechanisms like HTTP/REST, gRPC, or message queues for inter-service communication.
- Design asynchronous communication patterns to handle eventual consistency and decouple services.
Infrastructure and Deployment:
- Set up a container orchestration platform like Kubernetes for managing microservices deployment and scaling.
- Containerize microservices using tools like Docker to ensure consistent environments.
Security and Authentication:
- Implement security mechanisms like API gateways, authentication, authorization, and encryption for each microservice.
- Define and enforce access control based on roles and permissions.
Testing:
- Develop unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests for each microservice to ensure its functionality.
- Test inter-service communication and scenarios where multiple microservices interact.
Deployment Strategy:
- Plan deployment strategies such as blue-green deployments or canary releases to minimize downtime and disruptions.
- Create automated deployment pipelines for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD).
Monitoring and Logging:
- Implement monitoring and logging solutions to track the performance, health, and behavior of microservices.
- Use tools like observability platforms and centralized logging to troubleshoot issues.
Incremental Migration:
- Consider migrating one or a few modules at a time, instead of the entire monolith, to mitigate risks and learn from the process.
Data Migration:
- Migrate data from the monolith’s database to the microservices’ data stores. Use tools like ETL processes or batch migration scripts.
Rollout and Feedback:
- Gradually roll out microservices in production while monitoring their performance and user feedback.
- Gather feedback from users and stakeholders to make necessary adjustments.
Retire Monolith Components:
- As microservices become stable and mature, gradually retire corresponding components from the monolith.
Continuous Improvement:
- Continuously monitor the performance, scalability, and maintainability of microservices.
- Iterate and optimize based on lessons learned from migration and real-world usage.
Q. What type of business logic have you applied?
For the business logic I applied, the massage I got from IBM MQ I have to check the message size if the message size has greater than of certain number then I have to create a file in aws s3 and send that path into aws SQS as well otherwise I have to send only message into SQS
Q.What tools you have used in that project
- SonarLint is a static code analysis tool that helps developers identify and fix code quality and security issues early in the development process.
- Using OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) principles and guidelines in a Spring Boot application involves adopting best practices to enhance the security of your application. Ensure that the libraries and dependencies you use in your Spring Boot project are up-to-date and free from known security vulnerabilities.
- Nexus Repository serves as a central hub for managing software artifacts, which can include Java libraries (JARs), Docker images, Maven artifacts, NuGet packages, and more. It provides several key functionalities
Migrating a monolithic application to the AWS Cloud involves a series of steps to ensure a smooth and successful transition. Here’s a high-level overview of the process:
Assessment and Planning: Understand your monolithic application’s architecture, dependencies, and requirements. Identify the components that can be broken down into microservices or decoupled for better scalability, reliability, and maintainability. Create a detailed migration plan outlining the steps, timeline, resources, and potential challenges.
Choose AWS Services: Select AWS services that align with your application’s needs. Consider services like Amazon EC2, Amazon RDS, AWS Lambda, Amazon S3, Amazon ECS, AWS Fargate, and others based on your application’s requirements for compute, storage, databases, messaging, and more.
Containerization (Optional): If you’re considering a microservices architecture, containerize your monolithic application using technologies like Docker. This will make it easier to manage and deploy your application across different environments.
Decompose and Refactor: Break down the monolithic application into smaller, more manageable components. This could involve refactoring code, isolating functionalities, and defining clear APIs between components.
Data Migration: Migrate your application’s data to the AWS Cloud. Depending on your database, you might need to use AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) or tools specific to your database technology.
Security and Networking: Plan your network architecture and security measures. Use Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to isolate resources and control network traffic. Set up security groups, access control lists (ACLs), and other security mechanisms to protect your application.
Deployment and Scalability: Deploy your application using AWS services like Amazon EC2, Amazon ECS, or AWS Fargate. Utilize auto-scaling features to handle varying loads and ensure high availability.
Application Monitoring and Logging: Implement monitoring and logging solutions like Amazon CloudWatch to monitor the health, performance, and availability of your application. Set up alarms to be notified of potential issues.
Testing and Quality Assurance: Thoroughly test your migrated application in the AWS environment. Perform load testing, integration testing, and security testing to ensure everything works as expected.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Implement backup and disaster recovery strategies to safeguard your application’s data and ensure business continuity in case of failures.
Gradual Migration: Consider a phased approach for migration to reduce risks. You might start by migrating less critical components first to gain experience and confidence.
Training and Documentation: Train your team on AWS services and best practices for managing applications in the cloud. Document your new architecture, deployment processes, and operational procedures.
Go-Live and Monitoring: Gradually switch over to the cloud-hosted application once you’re confident that it’s running smoothly. Continuously monitor the application’s performance and address any issues that arise.
Optimization and Iteration: Continuously optimize your application’s performance and cost-efficiency. Use AWS tools and services to identify bottlenecks, scale resources as needed, and improve the user experience.
Migrating a monolithic application to the cloud is a complex process that requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing management. Consider collaborating with AWS experts or consulting professionals who have experience with similar migrations to ensure a successful outcome.
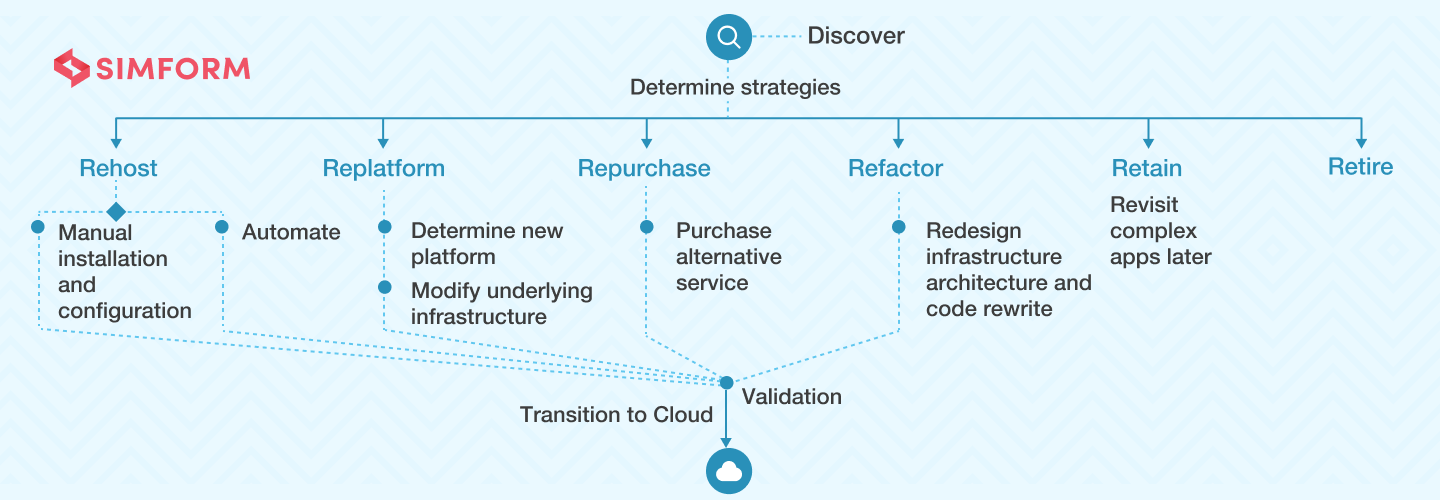
Migration strategies
Migration strategies refer to the various approaches and methodologies used to move applications, data, and workloads from one environment to another, such as on-premises to the cloud or from one cloud provider to another. Each strategy has its own advantages, challenges, and considerations. Here are some common migration strategies:
Lift and Shift (Rehosting): In this strategy, the application is migrated with minimal or no modifications from the source environment to the target environment. This approach is relatively quick and involves moving virtual machines, databases, and other resources to the cloud. While it offers faster migration, it might not take full advantage of cloud-native features and optimizations.
Replatforming (Lift, Tinker, and Shift): Replatforming involves making some adjustments to the application during migration to better align with cloud services and capabilities. This might involve optimizing the architecture, updating libraries, or modifying configurations. This strategy can provide a balance between quick migration and taking advantage of cloud benefits.
Refactoring (Re-architecting): Refactoring involves significant changes to the application’s architecture and code to fully leverage cloud-native services. This might include breaking down monolithic applications into microservices, using serverless computing, or optimizing for scalability and resilience. While refactoring offers the most benefits in terms of performance and scalability, it can be time-consuming and complex.
Repurchasing (Replacing): In this strategy, you replace the existing application with a commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) solution or a software-as-a-service (SaaS) offering. This is suitable when there are suitable alternatives available that meet your requirements without the need for extensive customization.
Retiring: This strategy involves discontinuing applications, services, or components that are no longer needed or relevant. It simplifies the migration process by reducing the scope.
Retaining (Revisit Later): For certain applications that are not suitable for migration immediately, the retaining strategy involves revisiting the migration decision in the future when the application or its dependencies are more cloud-ready.
Hybrid Strategy: A hybrid strategy combines multiple migration approaches based on the nature of the applications. Some components might be lifted and shifted, while others are refactored or replaced. This approach allows for a gradual migration and optimization over time.
Big Bang vs. Phased Approach: The big bang approach involves migrating the entire application in a single step, while the phased approach involves migrating components or modules in multiple stages. The choice depends on factors like complexity, risk tolerance, and the need for continuous operations.
Data Migration Strategies: For data migration, strategies like bulk data transfer, change data capture (CDC), or database replication can be used to move data from the source environment to the target environment. Data migration strategies should consider data consistency, downtime, and data integrity.
Project Migration Interview Questions
Lift and Shift (Rehosting)
1. What is lift and shift migration? Lift and shift migration, also known as rehosting, involves moving an application to the cloud without making significant changes to its architecture or code.
2. Why might you choose lift and shift migration? Lift and shift is chosen for quick migration when immediate benefits of cloud infrastructure are desired.
3. What challenges might arise during lift and shift migration? Compatibility issues, suboptimal resource utilization, and missed opportunities for optimization.
Replatforming (Lift, Tinker, and Shift)
4. What is replatforming in the context of migration? Replatforming involves making minor adjustments to an application during migration to better align with cloud services.
5. Give an example of a change made during replatforming. Updating database configurations for improved performance in the cloud environment.
6. What are the benefits of replatforming? Balances migration speed and cloud benefits, often providing better performance than lift and shift.
Refactoring (Re-architecting)
7. What is refactoring in migration? Refactoring involves making significant changes to an application’s architecture and code to leverage cloud-native features.
8. Why might you choose refactoring? To achieve scalability, improved performance, and take full advantage of cloud services.
9. What are the challenges of refactoring? Requires extensive code changes, thorough testing, and careful planning to avoid disruptions.
Data Migration Strategies
10. What is data migration in the context of project migration? Data migration involves moving data from one environment to another during migration.
11. What is bulk data transfer? Bulk data transfer involves moving large volumes of data using methods like physical shipping of storage devices.
12. Explain change data capture (CDC) in data migration. CDC involves identifying and capturing changes made to a database so that only updated data is migrated.
Hybrid Strategy
13. What is a hybrid migration strategy? A hybrid strategy combines multiple migration approaches based on application characteristics.
14. Why might you use a hybrid strategy? To balance quick migration of some components with optimized migration of others.
15. Give an example of a hybrid strategy. Lifting and shifting a web server while refactoring a database for better performance.
Big Bang vs. Phased Approach
16. What is the big bang migration approach? The big bang approach involves migrating the entire application in a single step.
17. What is the phased migration approach? The phased approach involves migrating components or modules in multiple stages.
18. What are the advantages of the big bang approach? Faster transition, but higher risk of disruption.
Application Testing
19. Why is testing important during migration? Testing ensures that the migrated application functions correctly in the new environment.
20. What is performance testing? Performance testing assesses the application’s speed, responsiveness, and stability in the new environment.
21. What is security testing? Security testing ensures that the migrated application remains secure and compliant.
Networking and Security
22. What is Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)? Amazon VPC is a network isolation mechanism in AWS that allows you to create private networks within the cloud.
23. Why is security important during migration? Security ensures the protection of data and resources during and after migration.
24. What are security groups in AWS? Security groups are virtual firewalls that control inbound and outbound traffic to AWS resources.
Monitoring and Optimization
25. Why is monitoring important after migration? Monitoring helps ensure that the migrated application performs well and remains available.
26. What is Amazon CloudWatch? Amazon CloudWatch is a monitoring and management service that provides insights into AWS resources.
27. How can you optimize cost after migration? Optimize cost by selecting appropriate instance types, leveraging auto-scaling, and reviewing resource utilization.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
28. Why is data backup important in the cloud? Data backup ensures that you can recover data in case of accidental deletion or corruption.
29. What is Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service)? Amazon S3 is a scalable storage service in AWS that can be used for data backup and recovery.
30. How can you ensure disaster recovery in the cloud? Create and test disaster recovery plans, implement backup strategies, and use multiple Availability Zones.
Change Management and Communication
31. Why is change management crucial during migration? Change management ensures that the migration process is well-documented and communicated to stakeholders.
32. How do you manage communication during migration? Regularly communicate progress, milestones, and any potential disruptions to stakeholders.
33. What is the importance of involving stakeholders in migration decisions? Involving stakeholders ensures alignment with business goals and expectations.
Training and Documentation
34. Why is training important after migration? Training ensures that your team is familiar with the new environment and can operate effectively.
35. What should documentation cover after migration? Documentation should cover architecture, configurations, operational procedures, and troubleshooting.
36. How can documentation help with knowledge transfer? Documentation helps new team members understand the migrated environment and processes.
Cloud Provider Lock-In
37. What is cloud provider lock-in? Cloud provider lock-in refers to the challenge of migrating away from one cloud provider to another due to platform-specific features.
38. How can you mitigate cloud provider lock-in? Use cloud-agnostic services and design architectures with portability in mind.
Cost Estimation and Management
39. Why is cost estimation important before migration? Cost estimation helps in budget planning and choosing the right services for your budget.
40. How can you manage costs after migration? Use cost management tools, review spending regularly, and optimize resources based on usage patterns.
Business Continuity and Downtime
41. Why is minimizing downtime important during migration? Minimizing downtime ensures that the application remains available and operational.
42. How can you achieve zero-downtime migration? Use strategies like blue-green deployment, canary releases, and data replication.
43. What is a rollback plan? A rollback plan outlines the steps to revert to the previous environment in case of issues during migration.
Integration with Existing Systems
44. How can you ensure integration with existing systems during migration? Test integration points thoroughly and ensure that APIs, data flows, and connections are functional.
45. What is an API gateway? An API gateway is a service that enables the exposure, management, and security of APIs.
DevOps and Automation
46. What is the role of DevOps in migration? DevOps practices automate and streamline the migration process, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
47. What is Infrastructure as Code (IaC)? IaC is a practice of managing and provisioning infrastructure using code.
48. How does automation help in managing cloud resources? Automation simplifies resource provisioning, scaling, and management tasks.
Documentation and Knowledge Transfer
49. Why is documentation important in knowledge transfer? Documentation preserves institutional knowledge and makes it accessible to team members.
50. How can you ensure knowledge transfer after migration? Provide training, maintain comprehensive documentation, and encourage knowledge sharing.
Testing and Rollback Planning
51. What is a testing environment? A testing environment is a separate environment used for testing changes before they are deployed to production.
52. How can you ensure a successful migration with minimal risk? Thoroughly test the migration process in a controlled environment before performing it in production.
53. What is a rollback plan and why is it important? A rollback plan outlines the steps to revert to the previous state in case migration issues arise.
Cloud Service Selection
54. What factors should be considered when selecting cloud services? Consider factors like application requirements, performance, scalability, security, and cost.
55. How can you choose the right cloud services for your project? Evaluate the available options, match them to your application’s needs, and consider long-term scalability.
Scalability and Performance
56. How can you ensure scalability in the cloud environment? Use auto-scaling groups and load balancers to automatically adjust resources based on demand.
57. What is Amazon Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)? Amazon ELB automatically distributes incoming traffic across multiple targets for better availability and performance.
58. How does the cloud help improve application performance? The cloud provides resources that can be easily scaled up or down to meet performance requirements.
Security and Compliance
59. Why is security important during migration? Security ensures the protection of data and resources during and after migration.
60. What is the shared responsibility model in cloud security? Cloud providers and customers share responsibilities for security, with the provider securing the infrastructure and the customer securing their applications and data.
61. How can you ensure compliance during migration? Implement security controls, encryption, and access management to meet compliance requirements.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
62. Why is disaster recovery planning crucial during migration? Disaster recovery planning ensures that the application can be quickly restored in case of disruptions.
63. What is a recovery time objective (RTO)? RTO is the maximum acceptable time it takes to restore a system after a failure.
64. What is a recovery point objective (RPO)? RPO is the acceptable data loss in case of a disaster. It indicates how frequently data should be backed up.
Training and Skill Development
65. Why is training important for the migration team? Training ensures that team members are familiar with the cloud environment and migration process.
66. How can you ensure team members are prepared for migration challenges? Provide training on cloud services, migration best practices, and problem-solving techniques.
Cloud Governance
67. What is cloud governance? Cloud governance involves defining policies, controls, and procedures to manage cloud resources effectively.
68. How does cloud governance impact migration? Cloud governance ensures that migration aligns with organizational policies and objectives.
69. How can you manage costs and resource allocation using cloud governance? Implement policies for resource tagging, cost allocation, and budget management.
Vendor Lock-In
70. What is vendor lock-in and how can it be mitigated? Vendor lock-in occurs when dependencies on specific cloud services make it difficult to switch providers. Mitigate it by using standard APIs, avoiding proprietary features, and planning for future flexibility.
71. How does avoiding vendor lock-in impact future migration? Avoiding vendor lock-in ensures that you can easily migrate to another provider or adapt to changing technology.
Performance Testing
72. What is performance testing in the context of migration? Performance testing assesses how well an application performs in terms of speed, responsiveness, and stability.
73. How can you conduct performance testing for a migrated application? Simulate various user loads to identify bottlenecks and performance issues in the new environment.
Data Integrity and Validation
74. Why is data integrity important during migration? Data integrity ensures that data remains accurate and consistent during migration.
75. How can you validate data integrity after migration? Compare data in the source and target environments to ensure that migration didn’t introduce errors.
Cross-Region Migration
76. What is cross-region migration? Cross-region migration involves moving resources and applications from one geographic region to another in the same cloud provider.
77. Why might you choose cross-region migration? To improve performance, reduce latency, or adhere to data residency regulations.
78. What challenges might arise during cross-region migration? Data transfer speed, network latency, and potential application adjustments.
Compliance and Data Privacy
79. How can you ensure compliance with data privacy regulations during migration? Implement encryption, access controls, and data classification to protect sensitive information.
80. What is the role of a data protection officer (DPO) during migration? The DPO ensures that data privacy regulations are followed, and sensitive data is handled appropriately.
Cloud Migration Risks
81. What are some common risks associated with cloud migration? Data loss, security breaches, service disruptions, and unexpected costs.
82. How can you mitigate migration risks? Thoroughly plan, test, and follow best practices for security, data protection, and disaster recovery.
Legacy System Integration
83. How can you integrate a migrated application with legacy systems? Use APIs, middleware, and integration platforms to establish communication between old and new systems.
84. What is an integration platform as a service (iPaaS)? iPaaS provides tools for building, deploying, and managing integrations between applications and services.
Cloud Provider Services
85. What AWS services can you use for database migration? AWS Database Migration Service, AWS DataSync, and AWS Snowball are some options for database migration.
86. How can you use AWS Lambda during migration? AWS Lambda can be used for serverless computing, event-driven processing, and automating tasks during migration.
87. What is AWS Elastic Beanstalk and how can it assist migration? AWS Elastic Beanstalk simplifies application deployment and management, helping migrate applications with less manual effort.
Change Management
88. What is the importance of change management during migration? Change management ensures that migration tasks are well-documented, communicated, and aligned with business goals.
89. How can you handle change resistance during migration? Involve stakeholders early, address concerns, and communicate the benefits of migration.
Multi-Cloud Migration
90. What is multi-cloud migration? Multi-cloud migration involves distributing resources and workloads across multiple cloud providers.
91. Why might you consider multi-cloud migration? To avoid vendor lock-in, leverage diverse services, and increase redundancy.
92. What challenges might arise during multi-cloud migration? Complexity in managing multiple environments, interoperability issues, and differing features.
Business Impact Analysis
93. What is a business impact analysis (BIA)? A BIA assesses the potential impact of disruptions on business operations and helps prioritize recovery efforts.
94. How can you perform a BIA for migration? Identify critical applications, dependencies, and user expectations to assess the impact of migration.
Compliance and Auditing
95. How can you ensure compliance during migration? Implement security controls, encryption, and access management to meet compliance requirements.
96. How does auditing help during migration? Auditing ensures that security measures, policies, and procedures are followed.
Cost Estimation
97. Why is cost estimation important during migration? Cost estimation helps in budget planning and choosing the right services for your budget.
98. How can you estimate migration costs accurately? Consider factors like data transfer, storage, compute resources, and licensing fees.
Continuous Monitoring
99. Why is continuous monitoring important after migration? Continuous monitoring ensures that the migrated application performs well and remains secure.
100. How can you ensure continuous monitoring of the cloud environment? Use tools like Amazon CloudWatch to monitor resources, set up alarms, and gather performance metrics.


Comments